A small rounding error hidden deep within Balancer’s smart contracts led to one of the largest decentralized finance (DeFi) exploits of 2025, draining more than $128 million from multiple blockchains’ Composable Stable Pools (CSPs).
The exploit began on November 3 at 07:46 UTC and was first detected by Hypernative’s automated monitoring system.
Minutes later, Balancer confirmed an active attack targeting its V2 Composable Stable Pools across networks including Ethereum, Base, Arbitrum, Avalanche, Optimism, Gnosis, Polygon, Berachain, and Sonic.
Notably, other types of Balancer pools and their associated V3 protocol were unaffected.
If Balancer has passed ten audits, what went wrong this time?
According to Balancer preliminary reportthe breach was caused by a small but critical rounding error in the ‘upscale’ function used during batch swaps, a feature that allows multiple token swaps in a single transaction.
The flaw occurred in the code that handled ‘EXACT_OUT’ swaps, where non-integer scaling factors caused rounding in the wrong direction, allowing attackers to manipulate pool balances and extract funds in rapid succession.
Balancer said the attack was limited to V2 Composable Stable Pools and their forks, such as BEX and Beets.
Initial assessments indicate that affected contracts were primarily those with expired pause windows, while newer CSPv6 pools were automatically paused by Hypernative’s emergency controls within minutes of detection.
Blockchain security firm PeckShield estimated total losses at more than $128 million, although Balancer said the exact figures have yet to be verified. Stolen assets, including ETH, osETH, and wstETH, were quickly bridged and partially laundered through Tornado Cash.
Balancer activated its emergency war room and coordinated with partners, whitehats and security teams to contain the attack.
The Safe Harbor Framework (BIP-726), introduced in 2024, allowed white hat responders to legally intervene and recover funds. Early recoveries include $19 million worth of osETH and $1.7 million worth of osGNO recovered by the StakeWise DAO.
Additional efforts within the DeFi ecosystem helped curb the losses. The Berachain Foundation conducted an emergency hard fork to capture stolen funds after a MEV bot operator agreed to return them.
Sonic Labs froze attacker wallets, while Gnosis and Monerium stopped approximately €1.3 million in EURe stablecoins to prevent cross-chain movements. Whitehat groups, including BitFinding and Base MEV bots, restored another $750,000.
In the latest update, Balancer noted that it had disabled the CSPv6 factory to prevent the creation of new pools, shut down liquidity meters for affected pools to stop emissions, and enabled the inclusion of liquidity providers in recovery mode.
Users with assets in paused pools can now withdraw their underlying tokens proportionately.
Balancer emphasized that its V3 pools and non-stable V2 pools remain unaffected and fully operational.
Balancer’s breach is related to a previously known rounding error: TVL plummets by more than 50%
The breach comes despite Balancer’s long-standing reputation for robust security. One of DeFi’s oldest automated market makers, the protocol has undergone more than ten audits by top companies including OpenZeppelin, Trail of Bits, and Certora.
Still, this latest exploit mirrors an earlier rounding-related vulnerability discovered in 2023, the same type of flaw that attackers have now used on a much larger scale.
Balancer has suffered several security incidents in its history, including a $520,000 loss in 2020, a $2.1 million loss rounding exploit in 2023, and a DNS hijack later that same year.
After the breach, the total value of Balancer (TVL) fell sharply from $442 million on November 2 to just over $214 million within 24 hours; it is now down to $182 million, according to to DeFiLlama.
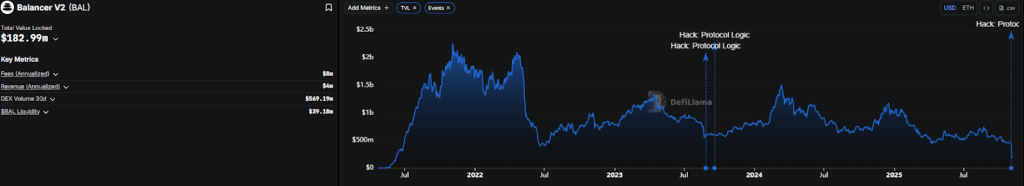
The impact sent shockwaves through the DeFi ecosystem, with a major whale wallet withdrawing $6.5 million shortly after the attack.
The post How a Small Rounding Error Fueled Balancer’s $128 Million Multi-Chain DeFi Exploit appeared first on Cryptonews.



